The primary difference between 4G and 5G is speed and latency. 5G offers faster speeds and lower latency compared to 4G.
5G technology is revolutionizing the way we connect and communicate. It provides significantly faster download and upload speeds than 4G. This results in smoother streaming, quicker downloads, and enhanced online gaming experiences. 5G’s lower latency means reduced lag, which is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous driving and telemedicine.
The network can handle more connected devices, making it ideal for smart cities and IoT applications. As 5G continues to roll out globally, it promises to transform various industries and improve everyday digital interactions. Understanding the differences between 4G and 5G helps consumers make informed decisions about their mobile and internet needs.
Introduction To 4g And 5g
Mobile networks have changed a lot over the years. 4G and 5G are two big steps in this change. They help us connect faster and do more with our phones. Let’s learn about their history and evolution.
Brief History
4G stands for the fourth generation of mobile networks. It started around 2010. It made the internet on phones much faster than before. People could stream videos and play online games easily.
5G is the fifth generation. It started to become available around 2020. It is even faster than 4G. It can connect many devices at once, like smart cars and home gadgets.
Evolution Of Mobile Networks
The journey to 5G began with 1G, the first mobile network. It only allowed voice calls. 2G added text messaging in the 1990s. 3G brought internet access to phones in the early 2000s.
| Generation | Key Feature | Time Period |
|---|---|---|
| 1G | Voice Calls | 1980s |
| 2G | Text Messaging | 1990s |
| 3G | Internet Access | 2000s |
| 4G | High-Speed Internet | 2010s |
| 5G | Ultra High-Speed, Many Devices | 2020s |
4G and 5G have made a huge impact. 4G allowed us to use apps like Uber and Instagram. 5G will help with things like self-driving cars and smart cities.
Each new generation of mobile networks brought new possibilities. 5G is the latest and the most advanced.
Basic Concepts
Understanding the difference between 4G and 5G is crucial. These terms relate to mobile networks. They define how our devices connect to the internet.
What Is 4g?
4G stands for the fourth generation of mobile networks. It succeeded 3G and brought faster speeds.
- 4G offers speeds up to 100 Mbps.
- It supports high-quality streaming and video calls.
- 4G introduced better connectivity and reliability.
4G uses LTE technology. LTE stands for Long-Term Evolution. It improved data transfer rates significantly.
What Is 5g?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks. It promises much faster speeds and lower latency.
- 5G offers speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- It supports ultra-high-definition streaming and virtual reality.
- 5G provides near-instantaneous communication.
5G uses new technology like millimeter waves and massive MIMO. These technologies enhance network capacity and performance.
| Feature | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 50 milliseconds | 1 millisecond |
| Technology | LTE | Millimeter waves, Massive MIMO |
Speed And Performance
The world of mobile networks is rapidly evolving. Speed and performance are crucial factors distinguishing 4G and 5G technologies. Understanding these differences can help users appreciate the advancements in mobile connectivity.
Download And Upload Speeds
4G networks offer decent speeds for most daily activities. Users can enjoy download speeds up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds up to 50 Mbps.
5G networks significantly enhance these speeds. Download speeds can reach up to 10 Gbps. Upload speeds can go up to 1 Gbps. These improvements enable faster file transfers and streaming.
| Network | Download Speed | Upload Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 4G | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 50 Mbps |
| 5G | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
Latency Differences
Latency refers to the delay before data transfer begins. 4G networks have an average latency of 50 milliseconds. This is suitable for most applications but can cause delays in real-time interactions.
5G networks drastically reduce latency. The average latency is around 1 millisecond. This makes real-time applications, like gaming and video calls, much smoother.
| Network | Latency |
|---|---|
| 4G | 50 milliseconds |
| 5G | 1 millisecond |
Speed and performance are key differences between 4G and 5G. Faster speeds and lower latency make 5G a game-changer in mobile technology.
Technological Advances
The transition from 4G to 5G brings significant technological advances. These advancements promise faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connections. Let’s explore some of the critical technological differences between 4G and 5G.
Network Architecture
4G networks primarily use macro cell towers. These towers cover large areas but can get congested. 5G, on the other hand, uses a combination of macro towers and small cells. Small cells are distributed more densely, providing better coverage and capacity.
- 4G: Relies on macro cell towers.
- 5G: Uses both macro towers and small cells.
Spectrum Utilization
4G and 5G also differ in how they use the radio spectrum. 4G mostly operates on lower frequency bands, which provide good range but limited speed. 5G uses a wider range of frequencies, including high-band millimeter waves. These high-frequency bands offer much higher speeds and capacity.
| Technology | Frequency Bands |
|---|---|
| 4G | Lower frequency bands |
| 5G | Low, mid, and high-frequency bands |
This diverse spectrum utilization allows 5G to support more devices and deliver faster data rates.
Use Cases And Applications
The transition from 4G to 5G is not just about speed. It’s about new possibilities. Let’s explore how these technologies impact our lives.
Current 4g Applications
4G technology has revolutionized how we use the internet. It supports a range of applications:
- Streaming Services: Watch videos on platforms like Netflix and YouTube.
- Social Media: Share photos and videos on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Mobile Gaming: Play multiplayer games with friends.
- GPS Navigation: Use maps for turn-by-turn directions.
- Video Calls: Communicate via apps like Zoom and Skype.
Emerging 5g Applications
5G technology is set to unlock new applications. These include:
- Smart Cities: Enhance traffic management and public services.
- IoT Devices: Connect more devices seamlessly.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Enable safer and smarter self-driving cars.
- Remote Surgery: Allow doctors to perform surgeries from afar.
- Enhanced VR/AR: Improve virtual and augmented reality experiences.
Impact On Everyday Life
The shift from 4G to 5G significantly alters our daily lives. This new technology promises faster speeds, lower latency, and more connected devices. Let’s explore how 5G affects us in different ways.
Consumer Benefits
5G offers many benefits to everyday users. Its faster speeds allow for quick downloads and uploads. Streaming high-definition videos becomes seamless with no buffering.
Lower latency means more responsive online gaming. Actions appear instantly, making games more enjoyable. Enhanced connectivity supports more smart devices at home. This makes your home smarter and more efficient.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) experiences become more immersive.
- Real-time communication with friends and family improves.
- Remote work becomes easier with stable, fast internet.
Industrial And Commercial Uses
5G impacts industries significantly. It enables smart factories with automated machines. These machines communicate in real-time, increasing efficiency.
In healthcare, 5G allows for remote surgeries. Surgeons can operate from miles away using robotic tools. Logistics benefit from real-time tracking of goods. This ensures timely deliveries and reduces losses.
| Industry | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated machines, real-time data |
| Healthcare | Remote surgeries, faster data transfer |
| Logistics | Real-time tracking, efficient delivery |
Retail also sees improvements with 5G. Stores use AR for enhanced shopping experiences. Customers can virtually try on clothes or see how furniture fits in their homes.
Agriculture benefits from smart farming. Sensors in fields provide real-time data on soil conditions. Farmers can then optimize watering and fertilization.
In transportation, 5G supports self-driving cars. These cars communicate with each other and the road infrastructure. This increases safety and reduces traffic congestion.
5G technology brings many changes to our everyday life. From consumer benefits to industrial uses, its impact is widespread and transformative.
Infrastructure Requirements
Understanding the infrastructure requirements of 4G and 5G is crucial. Both technologies need different setups to provide their services. Let’s explore the specific needs of 4G and 5G networks.
4g Infrastructure
4G networks rely on macro cell towers. These towers cover large areas. They use lower frequency bands. This helps them reach further distances. The infrastructure of 4G includes:
- Macro cell towers
- Base stations
- Antennas
- Backhaul connections
4G networks need fewer cell towers. They are designed for broad coverage. The deployment is less dense. This makes 4G setup easier and less costly.
5g Infrastructure
5G requires a denser network of small cell stations. These small cells are installed on streetlights, buildings, and other structures. The infrastructure of 5G includes:
- Small cell stations
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output)
- Beamforming technology
- High-frequency bands
5G uses high-frequency bands. These bands provide faster speeds but cover shorter distances. Therefore, 5G needs more small cells. This makes the deployment more complex and costly.
Below is a table comparing the infrastructure requirements:
| Feature | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Cell Type | Macro Cell Towers | Small Cell Stations |
| Frequency Bands | Lower Frequency | Higher Frequency |
| Coverage Area | Large | Small |
| Deployment Density | Less Dense | More Dense |
| Technology | Base Stations | Massive MIMO, Beamforming |
Both 4G and 5G have unique infrastructure needs. These needs shape their performance and deployment strategies.

Credit: dgtlinfra.com
Coverage And Availability
The coverage and availability of 4G and 5G networks vary significantly. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right network. This section dives into the current state of global 4G and 5G coverage.
Global 4g Coverage
4G networks are widely available across the world. Most urban areas have strong 4G signals. Rural areas also enjoy decent coverage. Mobile operators have spent years building 4G infrastructure.
Here is an overview of 4G availability:
| Region | 4G Coverage |
|---|---|
| North America | 95% |
| Europe | 90% |
| Asia | 85% |
| Africa | 70% |
Global 5g Rollout
5G networks are still expanding. Not all areas have 5G yet. Urban centers are the first to get 5G. Rural areas may wait longer.
Here is an overview of 5G rollout:
- North America: Major cities have 5G.
- Europe: 5G available in key cities.
- Asia: Rapid 5G expansion in cities.
- Africa: Limited 5G rollout.
The 5G rollout is ongoing. Expect more areas to get 5G soon. Check with your provider for updates.
Security Considerations
Security is a key factor when comparing 4G and 5G networks. The advancements in 5G promise enhanced security features. But, 4G still holds strong with its established measures. Let’s dive into the specifics of each.
4g Security Measures
4G networks use robust security protocols. These include:
- Authentication: Ensures only authorized users access the network.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted during transmission to protect privacy.
- Integrity Protection: Prevents data tampering during transmission.
4G also uses the EPS-AKA protocol. This protocol provides secure communication between users and the network.
Enhanced 5g Security
5G networks bring new security enhancements. These include:
- Improved Encryption: Stronger encryption algorithms protect data more effectively.
- Network Slicing: Creates isolated virtual networks for different services, enhancing security.
- Advanced Authentication: Uses multiple authentication steps for better security.
5G also introduces the SBA (Service-Based Architecture). This architecture enhances network security and efficiency.
Here’s a quick comparison table for better understanding:
| Feature | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Standard | Enhanced |
| Authentication | Single-step | Multi-step |
| Network Architecture | Traditional | Service-Based |
In summary, both 4G and 5G have strong security features. But 5G’s new enhancements promise even greater protection.
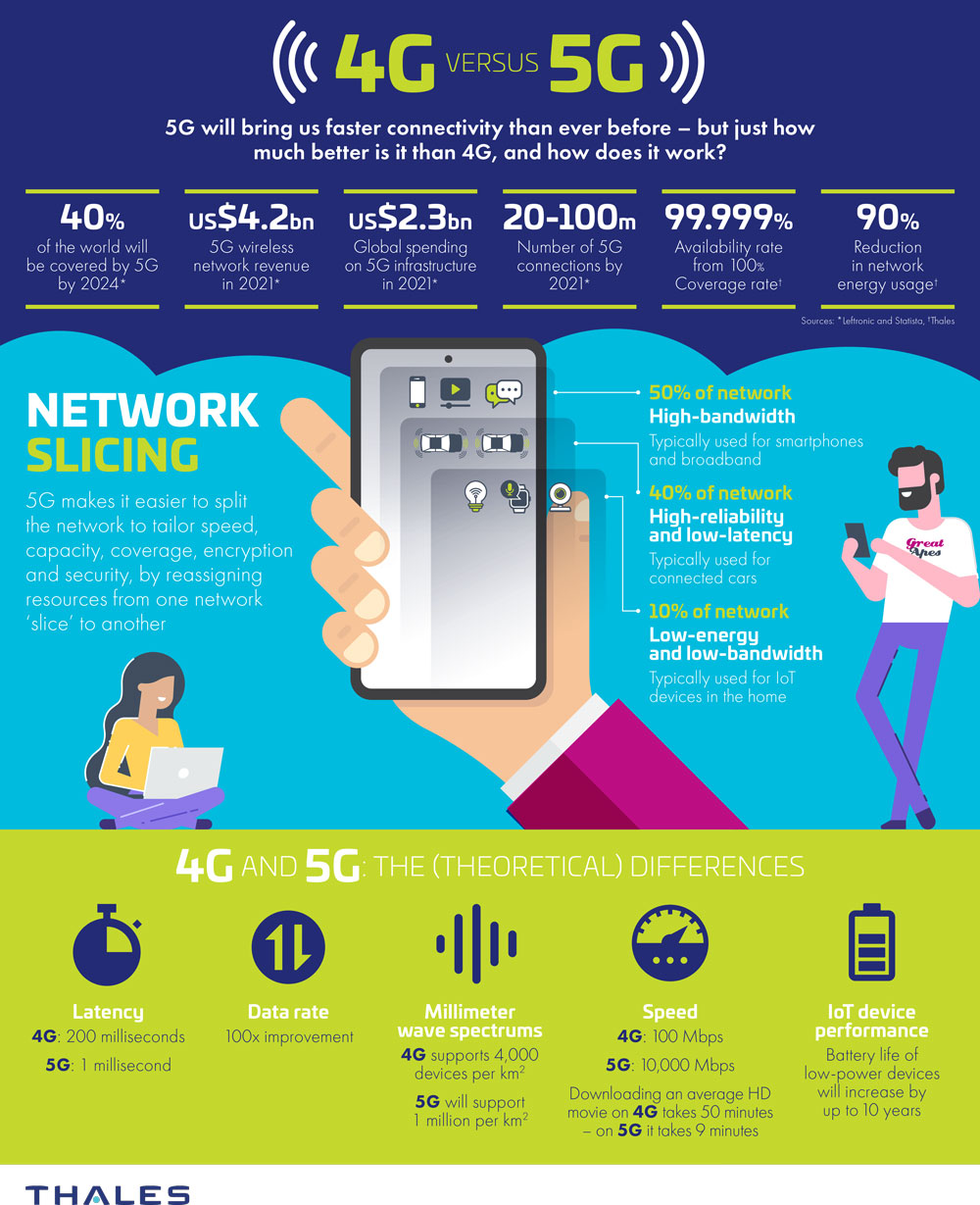
Credit: www.thalesgroup.com
Cost Implications
The shift from 4G to 5G brings significant cost implications. These affect both infrastructure and consumer expenses. Understanding these costs helps in making informed decisions.
Cost Of Implementation
Implementing 5G technology requires massive investments. Telecom companies need new infrastructure. This includes new towers and small cells. Upgrading existing equipment also adds to the cost.
| Cost Factor | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Moderate | High |
| Equipment | Existing | New |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
Infrastructure costs are higher for 5G. Companies need to build new towers and buy new equipment. Maintenance costs also increase due to the complexity of 5G systems.
Cost To Consumers
Consumers may experience higher costs with 5G services. This includes higher data plans and new 5G devices.
- Data Plans: 5G data plans are usually more expensive.
- Devices: New 5G smartphones and tablets are required.
- Speed: Faster speeds come at a higher price.
Consumers need to budget for these additional costs. Data plans for 5G often cost more due to higher speeds and bandwidth. 5G devices are also more expensive compared to 4G devices.
Despite the higher costs, many consumers prefer 5G for its faster speeds and better connectivity.
Future Prospects
The transition from 4G to 5G technology marks a significant leap in mobile connectivity. The future holds exciting developments, promising faster speeds and new possibilities for both consumers and industries.
Potential 5g Innovations
5G technology brings a host of potential innovations that were not possible with 4G. Here are some key advancements:
- Smart Cities: 5G can power interconnected systems for traffic management, utilities, and public safety.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Enhanced connectivity supports real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
- Remote Healthcare: Telemedicine and remote surgeries become more reliable with lower latency.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): 5G enables more immersive experiences with higher quality graphics.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Millions of devices can connect simultaneously, enhancing smart home and industrial applications.
4g’s Ongoing Relevance
While 5G offers groundbreaking innovations, 4G remains relevant and widely used. Here’s why:
| Aspect | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Extensive | Limited but expanding |
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 50 ms | 1 ms |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
4G networks are still evolving and improving. They are more accessible in remote areas. Many devices still rely on 4G for connectivity. The infrastructure for 4G is well-established, making it reliable. The transition to 5G will be gradual, ensuring 4G remains vital.
Challenges And Limitations
Both 4G and 5G technologies offer immense benefits. Yet, each has its own challenges and limitations. Understanding these issues is crucial for making informed decisions about mobile connectivity. Below, we will explore the specific challenges of both 4G and 5G networks.
4g Challenges
4G technology has revolutionized mobile connectivity. But it is not without its challenges:
- Network Congestion: High usage leads to slower speeds.
- Limited Coverage: Some rural areas lack 4G access.
- Latency Issues: Delays in data transmission affect real-time applications.
- Battery Drain: Constant 4G usage drains mobile batteries quickly.
5g Challenges
5G promises much faster speeds and lower latency. However, it also faces several challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Setting up 5G networks is very expensive.
- Limited Range: 5G signals do not travel as far as 4G.
- Device Compatibility: Older devices cannot support 5G technology.
- Security Concerns: Increased connectivity raises potential cyber-attack risks.
Below is a quick comparison of 4G and 5G challenges:
| 4G Challenges | 5G Challenges |
|---|---|
| Network Congestion | Infrastructure Costs |
| Limited Coverage | Limited Range |
| Latency Issues | Device Compatibility |
| Battery Drain | Security Concerns |
Both 4G and 5G have their own sets of challenges. Knowing these can help users and providers make better choices.
Conclusion And Summary
Understanding the difference between 4G and 5G is crucial. This helps in making informed choices about mobile networks. Below is a summary of the key differences and future prospects.
Key Takeaways
- Speed: 5G offers much faster data speeds than 4G.
- Latency: 5G has lower latency, which means quicker response times.
- Capacity: 5G can handle more devices connected at once.
- Technology: 5G uses advanced technologies like mmWave and MIMO.
- Applications: 5G supports new applications like autonomous cars and smart cities.
Looking Ahead
The future looks bright with 5G. It will revolutionize various industries. Expect new innovations in healthcare, transportation, and entertainment.
While 4G is still reliable, 5G offers more potential. Its higher speeds and lower latency will make a big difference. Keep an eye on the developments in 5G technology.
| Aspect | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 1 Gbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 50ms | 1ms |
| Capacity | Limited | Massive |
Stay informed and ready for the shift from 4G to 5G. The advancements are exciting and promising.
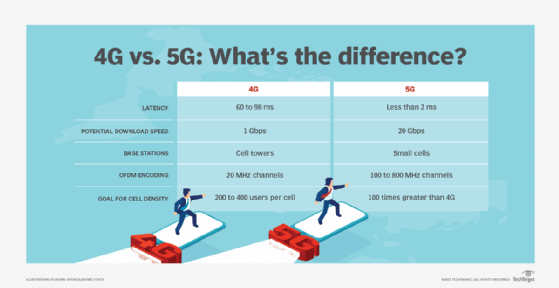
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is It Better To Get 4g Or 5g?
5G offers faster speeds and lower latency than 4G. If your area supports 5G, it’s the better choice.
Do I Really Need 5g?
5G isn’t essential for everyone. It offers faster speeds and lower latency, beneficial for gaming, streaming, and smart devices. If you rely on these, consider upgrading.
Can I Use A 5g Phone On A 4g Network?
Yes, you can use a 5G phone on a 4G network. It will connect to 4G without issues.
Will 4g Be Phased Out?
4G will not be phased out immediately. It will coexist with 5G for several years, ensuring broad coverage and support.
What Is 4g?
4G is the fourth generation of mobile network technology, offering faster internet speeds and improved connectivity.
What Is 5g?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks, providing higher data speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity.
How Fast Is 4g?
4G can reach download speeds up to 100 Mbps, but typical speeds are around 20-40 Mbps.
How Fast Is 5g?
5G can achieve download speeds up to 10 Gbps, significantly faster than 4G.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between 4G and 5G is essential. 5G offers faster speeds and lower latency. This revolutionizes connectivity. Transitioning to 5G promises enhanced experiences in various sectors. Stay informed to make the best decision for your needs. Embrace the future with 5G technology.
