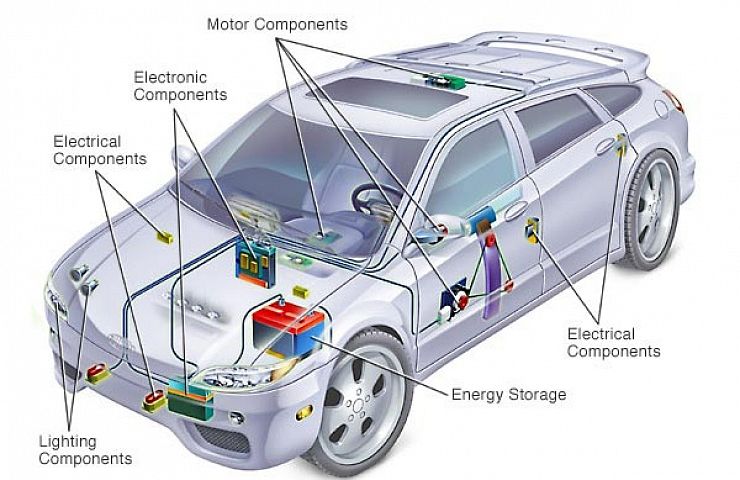
The automotive electrical system is crucial to modern vehicles. It powers everything from lights to the engine.
Understanding this system can save you time and money. It can help you diagnose problems before they become major issues. The electrical system includes the battery, alternator, starter, and more. Each part plays a vital role in your car’s performance.
Without it, your car wouldn’t function properly. This blog will explore the basics of the automotive electrical system. We will break down each component and its function. You’ll gain insights into how they work together to keep your car running smoothly. Let’s dive into the world of automotive electrical systems and learn how they power your ride.
Credit: toytechs.com
Introduction To Automotive Electrical Systems
Modern vehicles rely heavily on their electrical systems. Automotive electrical systems power everything from ignition to lights and entertainment. These systems are complex but crucial for vehicle performance and safety.
Significance In Modern Vehicles
Electrical systems are the backbone of modern vehicles. They enhance safety, comfort, and efficiency. Advanced systems like ABS, airbags, and navigation depend on reliable electrical components. This makes understanding these systems vital for anyone interested in cars.
Key Components Overview
Automotive electrical systems consist of several key components. These parts work together to ensure the vehicle runs smoothly. Below is an overview of the main components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for starting the engine and powering accessories. |
| Alternator | Charges the battery and powers the electrical system when the engine is running. |
| Starter Motor | Initiates engine operation by turning the engine over. |
| Fuses and Relays | Protect circuits from overcurrent and control the operation of electrical components. |
| Wiring | Connects electrical components and allows the flow of current. |
Each component has a specific role. Together, they ensure the electrical system functions properly.
- The Battery is the heart of the system.
- The Alternator keeps the battery charged.
- The Starter Motor gets the engine running.
- Fuses and Relays protect and control.
- Wiring connects everything.
Understanding these components helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance. This knowledge can save time and money in the long run.

Credit: www.monolithicpower.com
Battery: The Powerhouse
The car battery is the lifeblood of your vehicle’s electrical system. It powers everything from the engine to the smallest light bulb. Without a good battery, your car won’t start. It’s that simple. Understanding the types and proper maintenance of batteries ensures your car runs smoothly.
Types Of Batteries
There are several types of car batteries. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. Here are the most common types:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: These are the most common. They are reliable and affordable.
- AGM Batteries: Absorbent Glass Mat batteries are more expensive. They last longer and are maintenance-free.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are lightweight and have a long lifespan. They are used in electric vehicles.
Choosing the right battery depends on your vehicle and needs. Always check your car’s manual for recommendations.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of your car battery extends its life. Here are some simple tips:
- Check the Battery Terminals: Ensure they are clean and tight. Corrosion can cause poor connections.
- Test the Battery: Use a voltmeter to check the charge. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Keep the Battery Charged: Avoid leaving your car unused for long periods. A trickle charger can help maintain the charge.
- Inspect the Battery Case: Look for cracks or bulges. These can indicate a problem.
- Monitor the Water Level: For lead-acid batteries, ensure the water level is adequate. Use distilled water only.
Regular maintenance prevents many common battery problems. It also ensures your car starts every time.
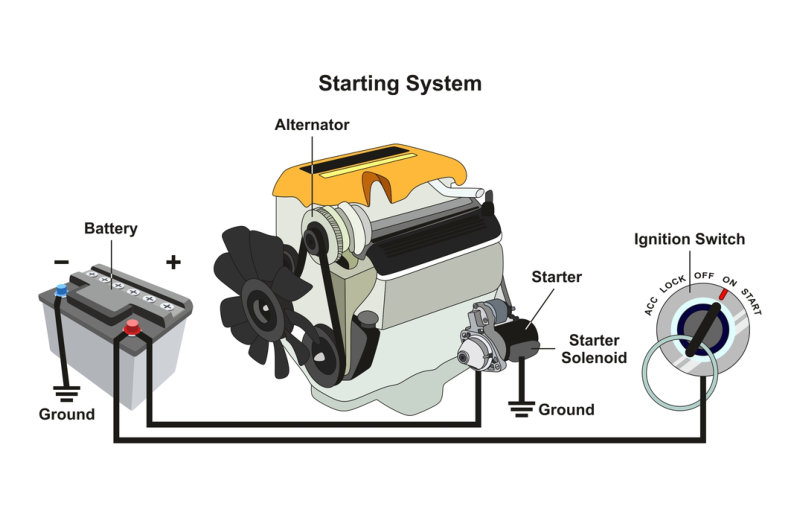
Alternator: The Charging System
The automotive electrical system is vital for vehicle operation. At the heart of this system lies the alternator. This device ensures your car’s battery stays charged and all electrical components function properly. Let’s delve deeper into the alternator’s role and how to spot issues.
Functionality And Importance
The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It does this while the engine runs. This energy powers your car’s electrical systems and recharges the battery. The alternator is essential for keeping the headlights bright, the radio playing, and the air conditioning running.
Without a functioning alternator, the battery would quickly drain. Your car would lose power and could leave you stranded. The alternator ensures a steady power supply, making it a crucial component of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Signs Of A Failing Alternator
Several signs indicate a failing alternator. One common sign is dimming headlights. If the lights flicker or appear dim, the alternator may not be providing enough power. Another sign is a dead battery. If the battery dies frequently, it might not be the battery at fault.
Strange noises can also signal trouble. Grinding or whining sounds from the engine area may point to alternator issues. Dashboard warning lights, such as the battery light, often indicate an alternator problem. Additionally, if your car stalls or struggles to start, the alternator could be failing.
Recognizing these signs early can prevent bigger problems. Regular checks and maintenance ensure the alternator remains in good working condition.
Starter Motor: Getting The Engine Running
The starter motor is crucial in getting your car’s engine running. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This process starts the engine’s ignition cycle. Understanding how it works can help you maintain your vehicle better.
Working Principle
The starter motor operates when you turn the key in the ignition. This action sends an electric current from the battery to the starter motor. The starter motor then spins the engine crankshaft. This action allows the engine to start. Once the engine runs, the starter motor disengages.
Common Issues
Starter motors can face several common issues. One of them is a dead battery. Without enough power, the starter motor can’t function. Another issue is worn-out solenoids. Solenoids relay the electric current to the starter motor. If they fail, the motor won’t receive power.
Another problem could be a faulty starter motor itself. Signs include a clicking sound when turning the key. This indicates the motor isn’t engaging properly. Regular maintenance can help avoid these issues. Check your battery and starter motor periodically. Doing so ensures your car starts smoothly every time.
Fuses And Relays: Safety Mechanisms
Fuses and relays play a crucial role in automotive electrical systems. They ensure the safety and smooth operation of various components. Without these mechanisms, electrical systems would be prone to damage and failure.
Role In Electrical Systems
Fuses protect electrical circuits from overloading. They break the circuit if the current exceeds safe levels. This prevents wires from overheating and causing fires. Relays, on the other hand, control high-power circuits using low-power signals. They act as switches, making it easier to manage complex electrical systems.
Together, fuses and relays maintain the integrity of the vehicle’s electrical network. They ensure each component receives the correct amount of power. This balance prevents damage and extends the life of the electrical system.
How To Diagnose Faults
Diagnosing faults in fuses and relays is essential for vehicle maintenance. Start by checking the fuse box for any blown fuses. A blown fuse will have a broken wire inside it. Replace any blown fuses with ones of the same rating.
For relays, listen for a clicking sound when the relay operates. No sound indicates a faulty relay. Swap the suspected relay with a known good one to confirm. If the system works with the new relay, the old relay is defective.
Regular checks of fuses and relays can prevent unexpected breakdowns. Keep spare fuses and relays in your vehicle for quick replacements. This practice ensures your vehicle’s electrical system remains reliable and safe.
Wiring And Connectors: The Nervous System
The automotive electrical system relies heavily on wiring and connectors. Think of them as the nervous system of a car. They transmit signals and power to all electrical components. Without them, nothing would function properly.
Wiring Harness Types
There are different types of wiring harnesses in a car:
- Main Wiring Harness: This connects all major electrical components.
- Engine Wiring Harness: This connects sensors and actuators to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Chassis Wiring Harness: This connects the electrical components on the car’s body, such as lights and sensors.
- Dashboard Wiring Harness: This connects the dashboard’s electrical components, including the instrument panel and infotainment system.
Connector Care And Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of connectors are crucial. Here are some tips:
- Regular Inspection: Check connectors for corrosion or damage.
- Clean Contacts: Use a contact cleaner to remove dirt and grime.
- Secure Connections: Ensure connectors are tightly secured to avoid loose connections.
- Use Dielectric Grease: Apply dielectric grease to prevent moisture and corrosion.
Maintaining the wiring and connectors in your car ensures a reliable and efficient electrical system. Follow these tips to keep your car’s nervous system in top shape.
Lighting Systems: Visibility And Safety
Lighting systems in vehicles play a crucial role in ensuring both visibility and safety. Proper lighting allows drivers to see the road and be seen by others. This reduces the risk of accidents, especially during low-light conditions. Effective lighting helps in navigating through fog, rain, and night driving. Thus, understanding automotive lighting systems is essential for every vehicle owner.
Types Of Automotive Lights
Cars have various types of lights, each serving a specific purpose. Headlights are the most common, providing forward illumination. They come in two main types: low beam and high beam. Low beams offer a short-range light, while high beams provide a long-range light. Tail lights are red and signal the car’s rear to other drivers. Brake lights are brighter and indicate slowing down or stopping.
Turn signals, or blinkers, show a vehicle’s intention to turn or change lanes. Fog lights are low-mounted and help in foggy conditions. Daytime running lights are automatically on during the day for visibility. Interior lights include dome lights and dashboard lights. Each type has a role in ensuring the driver and passengers’ safety.
Troubleshooting Light Issues
Light issues can arise, affecting visibility and safety. Start by checking the bulbs. Burnt-out bulbs are common and easy to replace. Inspect the fuses next. A blown fuse can cause lights to stop working. Replace it with one of the same rating.
Wiring problems can also lead to light issues. Look for loose connections or damaged wires. Sometimes, the issue lies in the light switch. If the switch feels loose or doesn’t click, it might need replacement. Regular maintenance helps prevent lighting problems.
Credit: www.ebay.com
Sensors And Actuators: Precision Control
In the modern automotive world, precision control is key. Sensors and actuators play a vital role in achieving this. They work together to ensure optimal vehicle performance. Understanding their functions helps in appreciating their importance.
Types Of Sensors
Sensors are devices that detect changes in the environment. There are various types used in automotive systems:
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor engine and cabin temperatures.
- Oxygen Sensors: Measure the oxygen level in the exhaust gas.
- Speed Sensors: Track the speed of the vehicle’s wheels.
- Pressure Sensors: Detect fluid and air pressure within the system.
- Position Sensors: Determine the position of various components.
Each sensor type serves a specific purpose. Together, they ensure the vehicle operates efficiently.
How Actuators Work
Actuators convert electrical signals into physical actions. They respond to signals from sensors and the control unit. The main types of actuators include:
- Electric Motors: Drive moving parts like windows and seats.
- Solenoids: Control valves and switches.
- Hydraulic Actuators: Use fluid power to move components.
- Pneumatic Actuators: Utilize compressed air for movement.
Actuators ensure precise movements and adjustments. They help maintain optimal vehicle performance.
| Sensor Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Monitors engine and cabin temperatures |
| Oxygen Sensor | Measures exhaust gas oxygen levels |
| Speed Sensor | Tracks wheel speed |
| Pressure Sensor | Detects fluid and air pressure |
| Position Sensor | Determines component positions |
In summary, sensors and actuators are crucial for vehicle precision control. They work together to monitor and adjust various systems. This ensures the vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
Ecu And Onboard Computers
The automotive electrical system is complex. One of its key components is the ECU, or Engine Control Unit. Onboard computers, like the ECU, play a crucial role in modern vehicles. They manage various functions to keep the car running smoothly. These systems improve performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
Functions Of The Ecu
The ECU controls many aspects of the engine. It regulates fuel injection, ignition timing, and idle speed. The ECU receives data from various sensors. It uses this data to make real-time adjustments. This ensures optimal engine performance. The ECU also monitors emissions to meet environmental standards. Additionally, it helps in diagnosing engine issues.
Diagnosing Ecu Problems
ECU problems can cause various issues in a vehicle. Common signs include the Check Engine Light turning on. Poor fuel economy and engine misfires are also indicators. Diagnostic tools can read error codes from the ECU. These codes help identify the specific problem. Fixing ECU issues often requires professional help. Regular maintenance can prevent many ECU problems.
Preventive Maintenance For Electrical Systems
A vehicle’s electrical system is its nervous system. Without it, nothing functions properly. Preventive maintenance is key to ensuring your vehicle’s electrical components work reliably. Regular checks and simple measures can prevent costly repairs and breakdowns. Below, we outline an effective preventive maintenance plan.
Routine Inspection Checklist
Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they become serious. Here’s a checklist for your vehicle’s electrical system:
- Battery: Check for corrosion and secure connections.
- Alternator: Ensure it charges the battery correctly.
- Fuses: Inspect for blown fuses and replace if needed.
- Wiring: Look for frayed or damaged wires.
- Lights: Verify all lights are functioning.
- Dashboard Indicators: Ensure all gauges and indicators work properly.
Common Preventive Measures
Simple actions can extend the life of your electrical system. Here’s what you can do:
- Battery Maintenance: Clean terminals and check water levels.
- Secure Connections: Tighten all electrical connections.
- Fuse Replacement: Always use the correct type of fuse.
- Insulate Wires: Use electrical tape for exposed wires.
- Check Belts: Ensure alternator belts are tight and in good condition.
By following these simple steps, you can keep your vehicle’s electrical system in top shape. Preventive maintenance not only saves money but also enhances safety on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Automotive Electrical System?
An automotive electrical system powers your car’s lights, radio, and other electronics.
How Does A Car Battery Work?
A car battery stores and provides electrical energy to start the engine and power accessories.
What Are Common Electrical Problems In Cars?
Common problems include dead batteries, faulty alternators, and blown fuses.
Why Is My Car Battery Draining?
Battery drain can be caused by leaving lights on, faulty wiring, or a bad alternator.
How Do I Check My Car’s Alternator?
Check the alternator by using a voltmeter. It should read between 13. 8 to 14. 2 volts.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bad Starter?
Symptoms include a clicking noise, slow engine crank, or no response when turning the key.
How Can I Prevent Electrical Issues In My Car?
Regular maintenance, checking connections, and ensuring the battery and alternator are in good condition.
Conclusion
Understanding the automotive electrical system is vital for every car owner. It ensures your vehicle runs smoothly and safely. Regular checks and maintenance can prevent many issues. This knowledge helps in better handling and troubleshooting. Keep learning and stay informed.
It makes your driving experience stress-free. Always prioritize your vehicle’s health. Safe driving!
